Newborn Physical Exam NCLEX Review for Nursing Students + Free Download
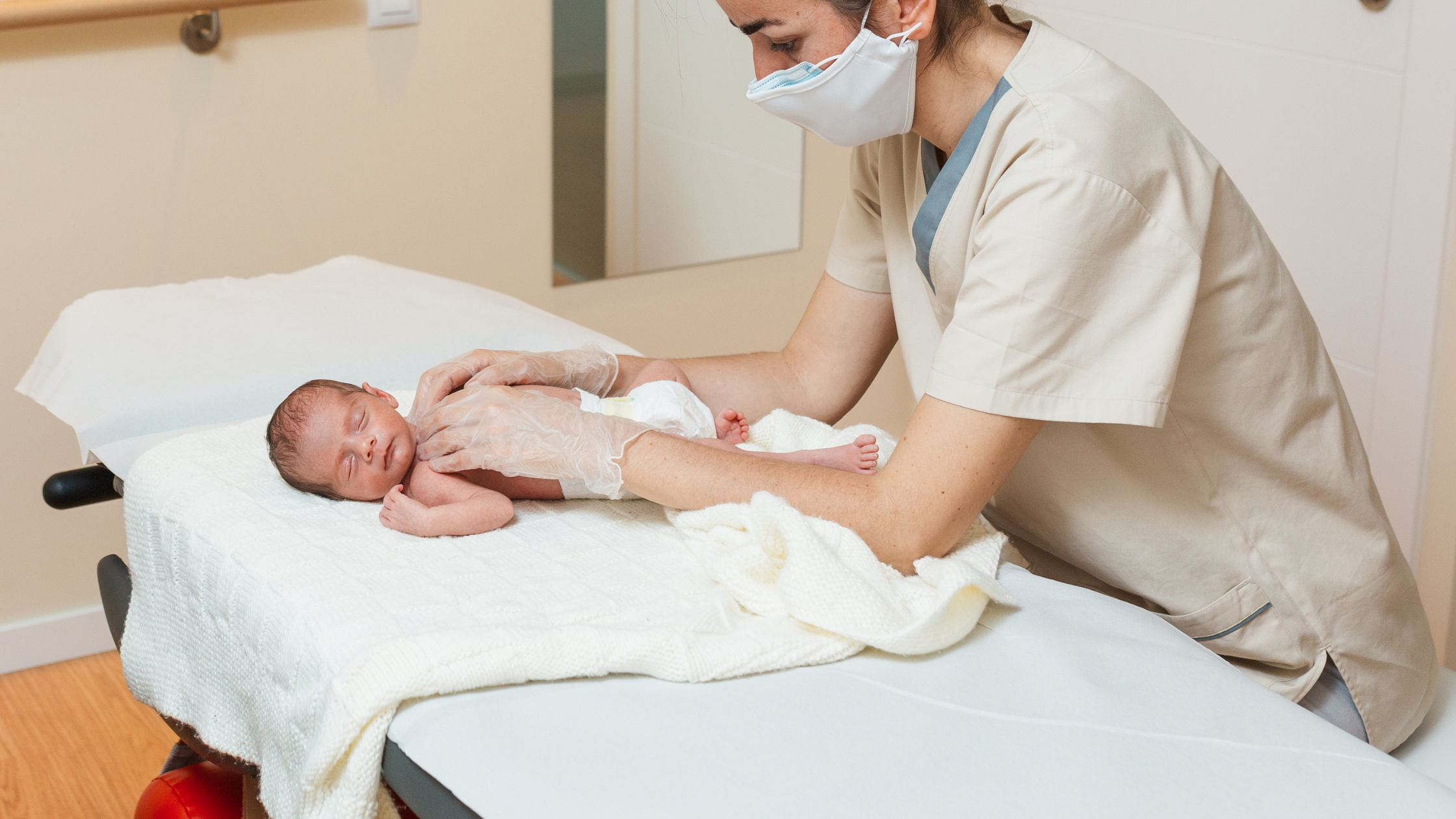

Understanding Newborn Physical Exam
Understanding the newborn physical exam is important for nursing students preparing for the NCLEX exam due to several reasons:
Assessment Skills: The newborn physical exam assesses the overall health and well-being of the newborn immediately after birth. Nursing students need to develop strong assessment skills to accurately identify any potential issues or abnormalities.
Early Detection of Complications: The newborn period is a critical time to identify any congenital anomalies, physical abnormalities, or signs of illness that require early intervention. Nurses must be able to recognize subtle signs of distress or abnormalities.
Communication: Nurses play a crucial role in communicating the findings of the newborn physical exam to the healthcare team, including pediatricians, neonatologists, and other specialists. Effective communication ensures timely and appropriate care.
Parent Education: Nursing students often educate parents about the findings of the newborn physical exam. Understanding the significance of each aspect of the exam allows nurses to explain the results to parents in a clear and empathetic manner.
Documentation: Accurate documentation of the newborn physical exam is vital for medical records, care planning, and continuity of care. Nurses need to know how to document findings comprehensively and accurately.
Infection Control: Nursing students need to practice strict infection control measures while performing the newborn physical exam to prevent the spread of infections and ensure the safety of both the newborn and the healthcare provider.
.png?width=1200&height=630&name=nclex%20review%20for%20angina%20(2).png)
Identification of High-Risk Newborns: Some newborns may require special attention due to prematurity, low birth weight, or other risk factors. Nurses need to be skilled at identifying these high-risk newborns and providing appropriate care.
NCLEX Preparation: The NCLEX exam may include questions related to the newborn physical exam, assessment techniques, normal findings, and potential abnormalities. A solid understanding of this topic is crucial for answering such questions accurately.
Patient Safety: Performing a thorough and accurate newborn physical exam contributes to patient safety by identifying issues that may require immediate intervention or ongoing monitoring.
Overall, understanding the newborn physical exam equips nursing students with essential skills and knowledge to provide high-quality care to newborns and their families. It ensures that nursing students are prepared to assess, communicate, and advocate for the well-being of the youngest and most vulnerable patients.
Overview of Newborn Physical Exam
1. These are the first physical assessments establishing a baseline is important!
2. Assess for temperature stability and note ALL abnormalities
General Information on Newborn Physical Exam
1. Keep baby warm!
a. It’s imperative that nursing interventions are
made to maintain temperature stability
2. The intrauterine – extrauterine transition period
a. 3 phases
i. Reactivity
1. Most alert and is the best feeding time
2. First hour
ii. Decreased responsiveness
1. Sleepy
2. Second hour
iii. Reactivity
1. Second reactivity
2. Hour 2-6
3. Alert
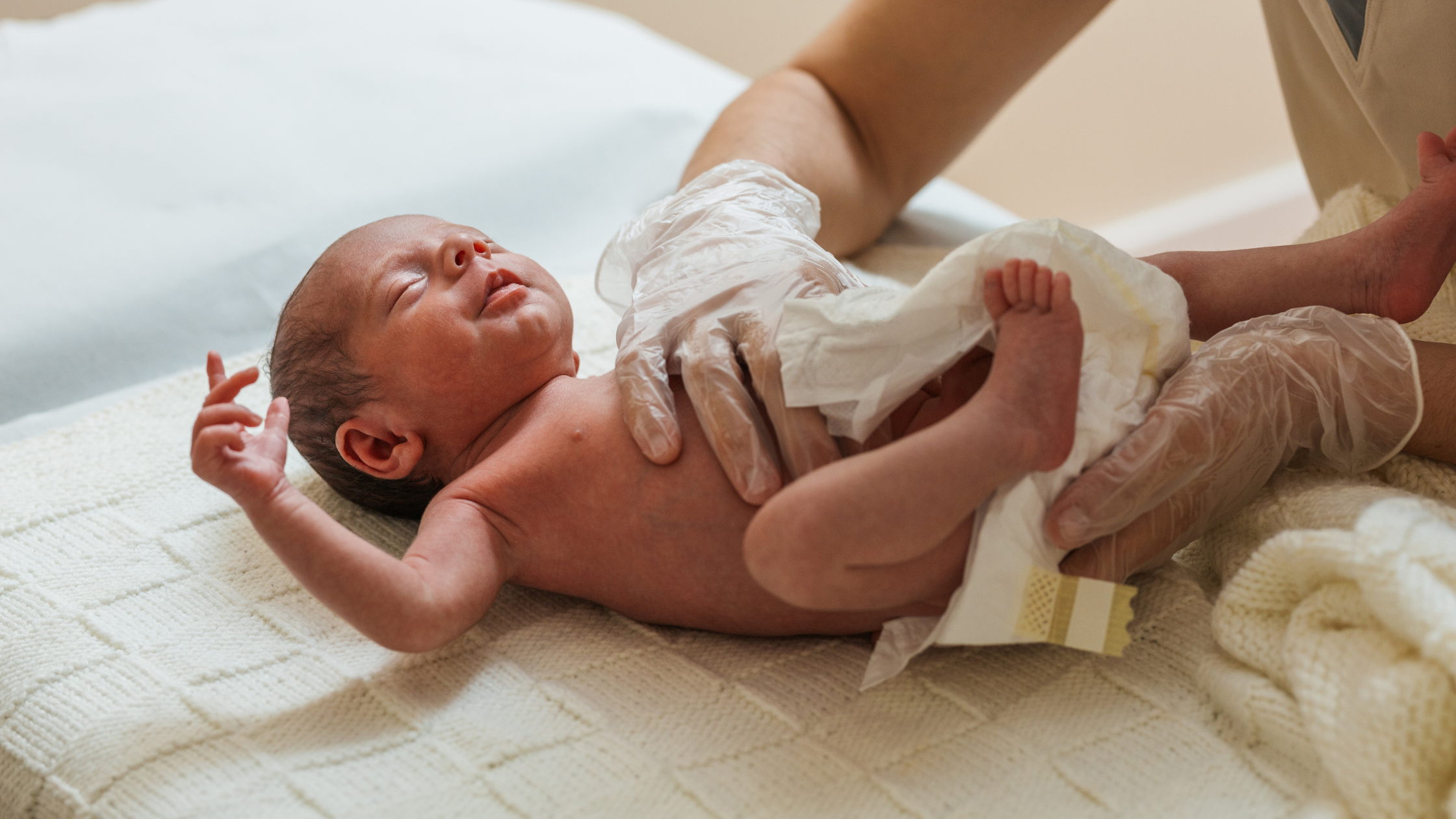
Nursing Assessment Newborn Physical Exam
1. General observations- Newborns should have a flexed posture &
coordinated movements
b. Count extremities, fingers, toes
c. Check for anus → not patent then DO NOT feed
i. If no anus is found, this results in an emergent surgery!
d. Urinary meatus on the penis if male
i. Hypospadias is meatus on the under portion
1. NO CIRCUMCISION can be performed on these clients
e. Check for hip dysplasia (hip pops)i. - Assessed with the Ortolani maneuver
1. Rotate thighs outward and feel for clicks at the hips,
2. NO clicking or crepitus is a normal finding
3. Any clicking or crepitus is indicative of hip dysplasia
4. Hip dysplasia is also checked by
putting the infant prone and looking for symmetrical butt creases
a. Symmetry indicates no dysplasia
Vital signs
a. Some newborns may present with slight/subtle
tremors
i. Can be normal or can be due to drugs
withdrawal, hypocalcemia, or hypoglycemia
b. Listen to apical pulse for 1 full min
i. 120-160 BP resting is a normal finding
c. Listen to respirations for 1 full min
i. 30-60 RR is a normal finding
d. Axillary temp
i. 97.8-99F is a normal finding
.png?width=1200&height=630&name=nclex%20review%20for%20angina%20(2).png)
Head
a. Measure head, weight, length
b. Fontanels (soft spot) anterior (back of the head)
and posterior (top of the head)
Eyes
a. Weak eye muscle
b. Newborns may have strabismus or disconjugate gaze
Ears
a. No pits or skin tags
Mouth
a. Assess for an intact palate, no teeth
Chest
a. Assess for clavicular fractures from birth
b. Breast tissue swelling might be observed
c. May note secretions from the nipple
Umbilical cord
a. Assess for 2 arteries and 1 vein
i. Assess for meconium staining on the cord
Genitalia
a. Female
i. blood-stained discharge may be present due
to a sudden decrease of estrogen
ii. might be swollen, prominent labia majora
b. Male
i. Hydrocele – excess fluid in the scrotum
Skin
a. Should have creases on hands and feet
i. More creases indicate an older gestational age
Possible skin findings in a newborn:
a. Erythema toxicum
i. Normal newborn rash→ Red spots that pop
up and move to different spots
b. Acrocyanosis
i. Blue extremities
ii. Normal for the first few days
c. Lanugo
i. Fine body hair
d. Harlequin Sign
i. Red/pink on one half of body
ii. Other half is normal or pallor is present
iii. Indicative of cardiac issues or sepsis
e. Milia
i. Small white sebaceous glands
ii. Typically noted on the face
f. Vernix caseosa
i. Protective mechanism
ii. White, cheese-looking substanceiii.
Term
1. Preterm – typically covered
2. Term – typically only in folds
3. Postterm – absent
g. Stork bites
i. Nape of neck, nose, eyelids
ii. Dark red – pale pink
h. Port-wine stain
i. Nevus vasculosus, typically on the face
ii. Flat, red-purple
iii. Technically a capillary angioma below the skin
i. Mongolian spots
i. On the back, bottom
ii. Black – blue
iii. Flat, wavy borders and irregular shape
iv. More common in darker races (African, Asian, Native American)
Conclusion and Free Download
This Newborn Physical Exam review provides essential knowledge for confidently approaching the NCLEX.
Are you looking for more must-know NCLEX review topics? Download our free eBook "NCLEX Flash Notes" as a valuable resource for nursing students. Encourage readers to download their free copy of the "NCLEX Flash Notes."
.png?width=1200&height=630&name=nclex%20review%20for%20angina%20(2).png)
You CAN Do This
Happy Nursing!





%20review%20nursing%20students.png?width=352&name=Intracranial%20Pressure%20(ICP)%20review%20nursing%20students.png)